Corneal Graft Surgery
What is Corneal Graft Surgery?
A corneal graft is also called a corneal transplant or keratoplasty. This procedure involves replacing a diseased or damaged cornea with a donated, healthy tissue cornea. One of the most common organ transplants that are performed today, corneal graft surgery is sight-restoring and has a high success rate. Most patients report improved vision after the surgery and a better quality of life.
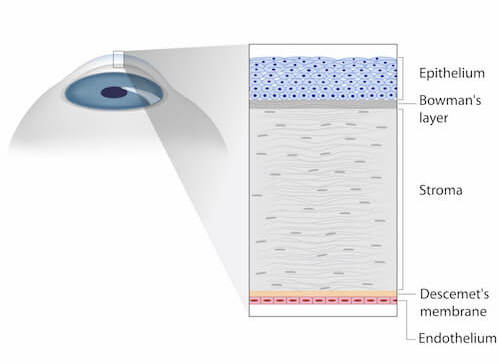
The function of the dome-shaped cornea is to prevent particles, dirt, germs, and UV light from entering the eyes and damaging them. Made up of three layers of tissue, the cornea works with the lens of the eyes to enable clear vision.
Ideal Candidates for Corneal Graft Surgery
The following symptoms indicate that a corneal transplant is required:
- Pain in the eyes
- Blurry vision
- Cloudy vision
During checkups, the ophthalmologist determines the cause of the problem and suggests possible treatments. A corneal transplant is done when all other options for treatment are not possible.
Certain medical conditions that lead to a damaged cornea include:
- Fuchs’s dystrophy
In this condition, the cells present in the inner layer of the cornea die and this makes the cornea swell and thicken which leads to blurred vision and difficulty in carrying out everyday activities.
- Keratoconus
This condition changes the shape of the cornea to become cone-shaped instead of remaining dome-shaped. The changed shape of the cornea makes it difficult to see and carry out normal activities.
Other conditions that damage the cornea include:
- Infections
- Traumatic injuries, especially those that penetrate or scar the cornea
- Previous eye surgeries that lead to complications
- Bullous keratopathy
- Keratitis
Any person who is suffering from Fuchs’ dystrophy, keratoconus, bullous keratopathy, keratitis, and eye infections will require corneal graft surgery to better or restore their vision. Also, people who have traumatic eye injuries need to opt for a corneal transplant.
A corneal transplant when done correctly and by experts corrects several issues of the eyes, some of which include:
- corneal scarring
- corneal ulcers
- keratoconus
- thinning, clouding, and swelling of the cornea
Estimated cost involved
Corneal graft surgery costs at least $5,000 per eye for those who do have private health insurance and those who choose their own eye surgeon to carry out the procedure. For public hospital patients, corneal transplants are covered by Medicare.
FAQ's
Before confirming the surgical plan, the surgeon and their anesthesia team go over your medical history and satisfy all patient queries, if any. Then anesthesia is administered, local or general depending on your medical history, following which medications are applied on the eye to numb it. The entire procedure hardly takes more than 2 hours and is done in an outpatient setting. No overnight stay is required.
In the first few days after the transplant, it is normal for the eye to be red, irritated, and sensitive to light. The eye is covered with an eye patch and protects the eye during sleep and showering. For the pain and temporary post-operative symptoms such as swelling, inflammation, and organ rejection, medications (antibiotics and corticosteroids), eye drops, and ointments are prescribed. Activities that could cause injury to the eye need to be avoided after the surgery, at least till the time the eye has completely healed.
The first follow-up visit is usually within 24-48 hours of the surgery. Glasses or some sort of protective eyewear need to be worn for a period of time till the eye heals. Rubbing or pressing the eye can cause damage and slow the process of healing.
While in most cases a corneal transplant has been known to improve vision and make the quality of life better, there have been a few instances where organ rejection was seen. This happens when the body’s immune system does not accept the donated cornea as its own and tries to fight it off as a foreign body. To manage such a situation eye drops are prescribed that need to be used for at least a year after the transplant to reduce the risk of corneal rejection.
Apart from rejection, there are a few other complications that can result after the corneal graft surgery:
- infection
- glaucoma or increased pressure in the eye
- bleeding
- clouding of the lens or cataract
- visual acuity problems
- corneal swelling
- corneal transplant detachment
- detached retina
- leakage of fluid from the cornea
Get in touch with your eye doctor immediately if you notice any of the following symptoms:
- Loss of vision
- Pain in the eye
- Sensitivity to light
Driving on the day of the transplant is totally out. Have someone assist you to your home and then again drive you back for the follow-up visit. If the vision in the other unoperated eye is normal and good, people usually can drive 24 hours after the surgery, but it is always best to avoid driving for at least a week after surgery or till the eye patch comes off from the operated eye.
